Pig Infected Wound Healing
Duration of study – 21 days
Lead time – 30 days
Standard results – Wound size measurements, Microbiology, Histology
Model Utility:
The pig infected wound model is a highly published and highly regarded model replicating human infected wound healing. Pigs are used because of their skin's anatomical and biochemical similarities to human skin and are the recommended model for use in evaluating wound healing and antimicrobial drugs and dressings, according to the FDA.
Of all the animal infection models that BRIDGE PTS offers, we have found this model to be the most difficult for new technologies to defeat!
How the Model Works:
Create full-thickness wounds
Typically infected with Staphylococcus epidermidis and/or Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Other microbes can be used such as Candida alibicans, Escherichia coli, and Klebsiella pneumoniae.
Treatment can begin any time during study (Anti-biofilm actives typically start after 48 hours)
Periodic sampling for bioburden of infected wounds via both non-selective and selective media.
Example Data:
The following are real data generated during studies. Due to confidentiality, we cannot disclose any of the test articles being evaluated. What sets each study data apart from the others is the duration that is waited before treatment begins. The longer treatment is delayed, the more difficult the infection is to treat.
Example Experiment 1:
"Planktonic bacteria"
Two-drug combination study
Wounds infected with Staph epi only
Leave-in daily treatments began on Day 0 (infection day)
Sampling performed on Days 0, 1 and 2
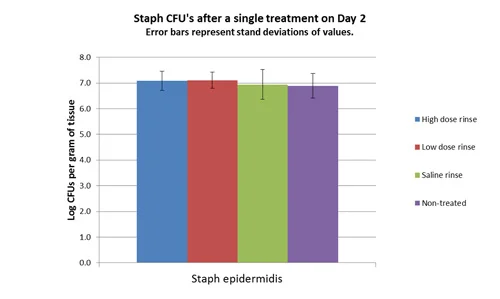
Example Experiment 2:
"Biofilm bacteria"
Single treatment "antiseptic" study
Wounds infected with Staph epi and Pseudomonas
Rinse treatment occurred on Day 2 (48 hours after infection was created)
Sampling performed on Day 2 immediately after treatment
Example Experiment 3:
"Planktonic & biofilm bacteria"
Single dose "long acting drug" study
Wounds infected with Staph epi and Pseudomonas
Leave-in treatment occurred on Day 0 (immediately), Day 0 (2 hrs post-infection) or Day 2
Sampling performed on Day 2
pathology is always available upon request:
Biofilm in an infected, non-treated wound 5 days after inoculation with Staph and Pseudomonas
References:
Wright JB, Lam K, Buret AG, Olson ME, Burrell RE. Early healing events in a porcine model of contaminated wounds: effects of nanocrystalline silver on matrix metalloproteinases, cell apoptosis, and healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2002 May-Jun;10(3):141-51
Olson ME, Wright JB, Lam K, Burrell RE. Healing of porcine donor sites covered with silver-coated dressings. Eur J Surg. 2000 Jun;166(6):486-9.